Ever wondered why the efficiency of electric motors isn’t always up to the mark? Iron losses might be the culprits behind this energy drain, but the good news is, they can be tackled effectively.
In this blog post, you’ll discover the different types of iron losses, understand why they occur, and learn practical strategies to minimize them.
By the end, you’ll be equipped with knowledge to enhance motor performance, reduce energy consumption, and possibly cut down on your energy bills. Stay tuned to turn these insights into action!
Types of Iron Losses in Electric Motors
Iron losses in electric motors can seem like a bit of a mystery, but breaking them down makes them easier to understand and manage. Let’s dive into the types you need to know about.
Hysteresis Losses
These occur due to the resistance of the motor’s core material to changes in magnetic fields. Every time the magnetic field changes direction, the molecular structure of the core material lags slightly behind, causing energy to be lost in the form of heat. It’s like trying to persuade a stubborn mule to change direction—there’s going to be some resistance!
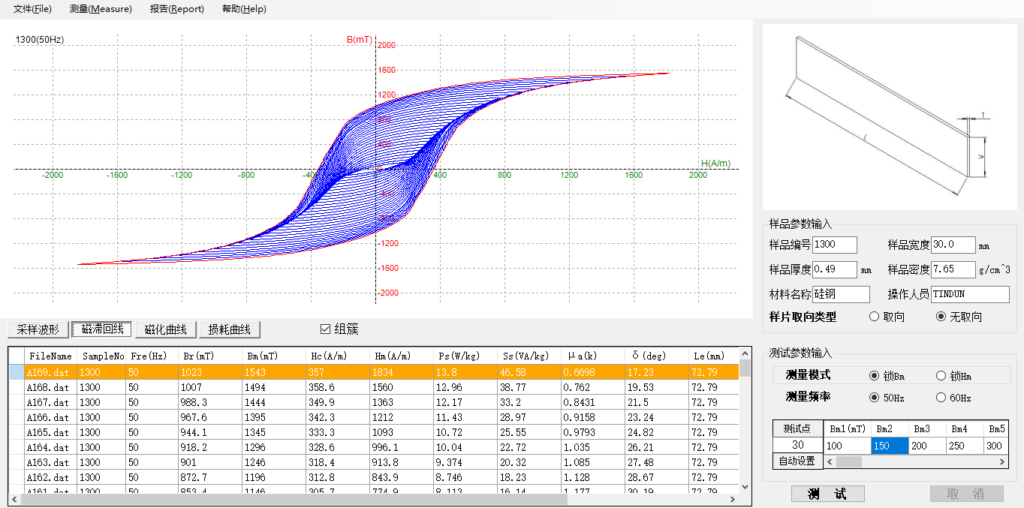
Eddy Current Losses
These are caused by circulating currents generated within the motor’s core as the magnetic field changes. Imagine swirling water in a cup—the currents move against the main flow, creating friction and, thus, heat. Reducing these currents is crucial, and it’s typically done by using thinner core laminations, which restrict the flow of these eddy currents.
Additional Losses
Additional losses, which might include stray losses due to the leakage of magnetic fields outside the intended path. These are the sneaky ones, often small but still impactful. Managing them involves precision in the motor’s design and assembly.
By understanding these losses, we can start to consider how to reduce them, which we’ll explore next. Each type has its own set of strategies for minimization, helping to boost the overall efficiency of the motor.
Factors Affecting Iron Losses
Several factors influence iron losses in induction motors. Understanding these can help in designing more efficient systems:
Core Material Properties: The type and quality of the material used in the motor’s core significantly affect core losses. Materials with lower hysteresis loss coefficients are preferred to minimize energy dissipation during magnetic field reversals.
Motor Design: The overall design of the motor, including the shape and size of the core as well as the arrangement of stator and rotor slots, influences how magnetic fields are distributed and, consequently, how core losses are incurred.
Operational Frequency: Higher frequencies increase both hysteresis and eddy current losses because the magnetic field changes direction more rapidly, giving less time for the material to respond without loss.
Lamination Quality: High-performance and thinner laminations in the core can reduce eddy current losses significantly. This is because thinner laminations restrict the flow of eddy currents, minimizing the resultant heat generation.
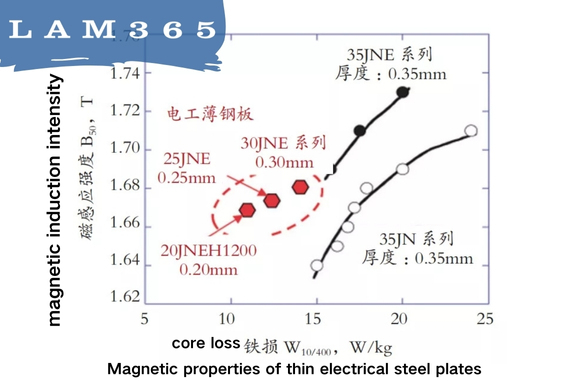
Temperature: Elevated operating temperatures increase the resistance of the core material, which in turn can increase hysteresis losses. Effective cooling systems are essential to maintain optimal performance and minimize losses.
By addressing these factors, motor designs can be optimized to reduce iron losses, enhancing efficiency and performance.
How to Reduce Iron Losses in Motors?
Reducing iron core losses in motors isn’t just a technical necessity—it’s also a cost-saving strategy! Here’s how you can tackle these losses efficiently:
Choose the Right Materials: Opt for high-quality magnetic materials specifically designed for low core losses. Are you using the best materials available for your motor’s core? If not, it might be time for an upgrade.
Enhance Motor Design: Reevaluate your motor design. Could tighter tolerances and improved slot design reduce stray flux and, thereby, core losses? Sometimes, small design tweaks can lead to big efficiency gains.
Innovate with Lamination Techniques: Implement advanced lamination techniques. Thinner laminations can drastically reduce eddy current losses. How thin are your current laminations, and could you benefit from going thinner?
Control Operating Frequency: Consider the operational frequency of your motor. Lower frequencies can reduce motor losses, but is this feasible for your application? If not, other methods might need to be prioritized.
Maintain Optimal Temperature: Keep your motor cool. Effective cooling systems prevent the core material’s resistance from increasing, which in turn keeps iron losses in check. What’s your current cooling strategy, and could it be improved?
Engage with these strategies to not just enhance motor performance but also potentially save on operational costs. What steps will you take first to reduce core losses in your motors?
What Is the Difference Between Copper Losses And Iron Losses in Brushless Motors?
In brushless motors, copper losses arise from the resistance in the motor’s windings, causing heat as current flows through them. Core losses, on the other hand, result from magnetic phenomena in the motor’s core, including hysteresis and eddy currents. While copper losses vary with the load, iron losses are more influenced by the motor’s magnetic and physical properties.
Conclusion
We’ve explored the nuances of iron losses in electric motors, understanding hysteresis, eddy current, and additional losses. By choosing the right materials, optimizing motor design, using advanced lamination techniques, controlling operational frequency, and maintaining optimal temperature, you can significantly reduce these losses, enhancing motor efficiency and performance.
Ready to supercharge your motor’s performance with customized solutions? Contact us today for tailored electrical steel motor lamination stacks that meet your specific needs. Let’s optimize your operations together!



