Have you ever wondered why electric vehicles (EVs) are becoming increasingly efficient and powerful? The secret lies in the heart of their motors—thin gauge electrical steel laminations. This blog will dive deep into thin gauge electrical steel and uncover its pivotal role in enhancing EV motor performance.
You’ll learn about the unique properties of this material, its impact on energy efficiency, and how it shapes the future of electric vehicles. By the end of this post, you’ll understand why this material is a game-changer for EVs and how it can potentially influence the sustainability and performance of future transportation technologies.
What is Thin Gauge Electrical Steel?
What exactly is Thin Gauge Electrical Steel? Commonly referred to as silicon steel or silicon electrical steel, this specialized material is a cornerstone in the electrical industry. Produced by cold-rolling silicon steel sheets, thin gauge electrical steel achieves a precise thickness generally between 0.1mm and 0.35 mm.

This steel is indispensable for manufacturing transformer cores and various electrical equipment, owing to its unique magnetic properties.
As a ferromagnetic material, it incorporates a significant silicon content, ranging from 2% to 4.5%. This addition of silicon enhances the steel’s electrical resistance and improves its magnetic properties, making it ideal for high-efficiency electrical applications.
Benefits of Using Thin Gauge Silicon Steel Laminations in New Energy Vehicle Motors
Using thin gauge electrical steel in electric vehicle (EV) motors offer several significant benefits that enhance both the performance and efficiency of these modern transportation solutions. Here’s how this specialized material makes a difference:
Low Core Loss:
One of the standout advantages of thin gauge electrical steel is its ability to maintain low core losses, especially at high frequencies. This characteristic is crucial for improving the efficiency of EV motors, as it minimizes energy wastage during the conversion of electrical energy into mechanical power. As a result, vehicles equipped with motors using this steel can enjoy reduced energy consumption, which is pivotal for extending the range and sustainability of EVs.
High Permeability:
This steel is also known for its high magnetic permeability, making it ideal for shielding applications within the motor. The high permeability ensures that the magnetic field is effectively confined, enhancing the motor’s electromagnetic performance and overall efficiency.
High Saturation Flux Density:
The ability to reach high saturation flux density allows EV motors to operate at higher efficiencies. This property is critical for designing downsized yet powerful high-frequency reactors and transformers, essential components in the compact yet robust motor design typical in modern EVs.
Excellent Insulation Coating:
Lastly, thin gauge electrical steel typically comes with superior insulation coatings. These coatings not only protect the core material but also enhance its performance through stress relief annealing. The result is an improved lamination factor, which contributes to the overall efficiency and durability of the motor by preventing electrical losses between the laminations.
To create an interference-free bond between electrical steel strip sheets, the strips can be coated with an adhesive varnish. Glue bonding or self-bonding methods can be used. This prevents the “frequency buzz” caused by welding, riveting, or stamping. Furthermore, the use of bonding varnishes does not hurt efficiency compared to conventional joining technologies.
Thin Gauge Electrical Steel Grades for High-Frequency Electric Motor
With the development of EV drive motors becoming smaller and faster, there will be an increasingly urgent need to reduce the high-frequency iron loss of electrical steel plates used in EV drive motor cores. The eddy current loss of high-frequency current is proportional to the square of the thickness of the electrical steel plate. Therefore, reducing the thickness of electrical steel plates is an effective way to reduce iron losses.
To this end, JFE has developed electrical thin steel plates, including electrical thin steel sheets with thicknesses of 0.20mm, 0.25mm, and 0.30mm.
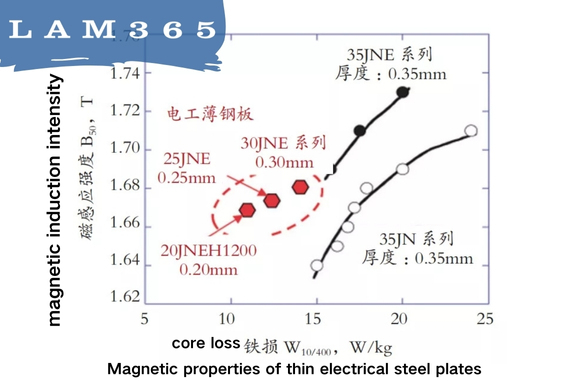
As can be seen from the picture, the iron loss of electrical thin steel plates with a thickness of 0.2mm is 25%-30% lower than that of the highest-grade electrical steel plates with a thickness of 0.35mm. Moreover, the higher the current frequency, the more significant the iron loss reduction effect of thinning the steel plate thickness is.
Conclusion
The performance requirements of electrical steel plates for EV (electric vehicle) drive motor cores are diverse. The drive motor should have high torque when starting and accelerating the EV, so the electrical steel plate for the iron core should have high magnetic induction intensity under high magnetic fields. Thin silicon steel laminations are the best choice.
With its low core loss, high permeability, and excellent insulation properties, it stands at the forefront of motor and generator technology. This material not only powers today’s electric vehicles but also shapes the future of automotive engineering.
Interested in optimizing your motor stator and rotor designs with high-performance electrical steel? Contact us today to explore our custom electrical steel motor lamination stacks tailored to your specific needs. Let’s drive innovation together!



