Have you ever wondered how to make motors smaller without sacrificing power? As a seasoned motor manufacturer and designer, I’ve spent years tinkering with motors to make them more compact and efficient. Today, I’m excited to share some insider tips to reduce motor size with you.
Reducing motor size isn’t just about squeezing components together; it’s a precise science that involves innovative techniques and cutting-edge technologies. Whether you’re a fellow engineer or just curious about motors, this guide will walk you through the essential methods to shrink those bulky motors down to size, all while keeping performance in check. Let’s dive in and uncover the secrets to making motors lean and mean!
Understanding Motor Size and Factors Affecting It
When it comes to motor size, understanding the basics is crucial. Motor dimensions are typically described by length (L) and diameter (D). These measurements dictate the motor’s physical footprint. The length-to-diameter ratio is especially important because it affects the motor’s efficiency and performance characteristics. A well-balanced ratio can optimize the motor’s capabilities.
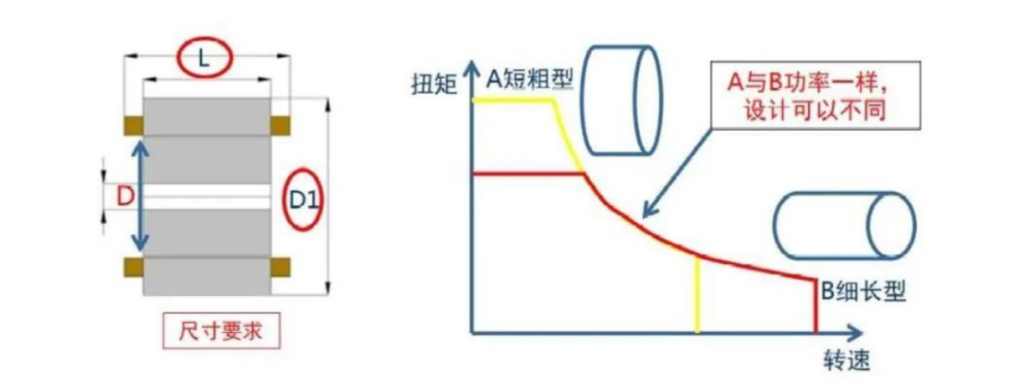
Several key parameters influence motor size.
The power, speed, and torque relationship is a fundamental consideration. Higher power and torque usually require larger motors, but optimizing speed can help reduce size.
Additionally, magnetic and electric load considerations play a significant role. Efficient management of these loads can lead to more compact and powerful motors, making them ideal for various applications.
Methods to Reduce Motor Size
1. Increasing Output Power Without Increasing Volume
As we all know, a motor’s power equals speed times torque. The volume of a motor isn’t directly related to its power output. To reduce motor size, we need to boost output power without increasing the volume. This means enhancing magnetic and electric loads and optimizing speed. By increasing the magnetic load (the magnetic field strength) and electric load (the current), we can achieve higher power output in the same physical space. Consequently, if the output power remains constant, the motor’s volume can be reduced. This approach allows for more compact and efficient motors without sacrificing performance.
2. High-speed bearings and Dynamic Balance
High-speed bearings are a game-changer for reducing motor size. These bearings can handle greater rotational speeds, which allows the motor to generate more power without increasing its size. Additionally, achieving dynamic balance in the motor’s rotating components minimizes vibrations and wear. This balance not only improves the motor’s efficiency but also prolongs its lifespan. By using high-speed bearings and ensuring dynamic balance, we can design smaller motors that perform exceptionally well under demanding conditions.
3. Improving Magnetic Flux Density
Improving magnetic flux density is another effective way to reduce motor size. Using advanced magnetic materials, such as rare-earth magnets, enhances the motor’s magnetic field strength. These materials allow for a higher flux density in the same volume, leading to increased torque and power output. Strategies like optimizing the motor’s magnetic circuit design and minimizing magnetic losses also contribute to higher flux density. As a result, motors can be made smaller and more powerful, making them suitable for a wide range of applications.
4. Innovative Cooling Techniques
Effective cooling techniques are essential for reducing motor size. Traditional air cooling can be bulky and inefficient, so innovative methods like oil cooling are gaining popularity. Oil cooling not only dissipates heat more effectively but also allows for a more compact motor design. Enhanced cooling improves the motor’s efficiency and prevents overheating, which is crucial for maintaining performance in smaller motors. By adopting advanced cooling techniques, we can achieve significant size reductions without compromising on power.
5. X-PIN flat Wire Winding Technology
X-PIN flat wire stator technology plays a crucial role in motor size reduction.
Unlike carbon fiber high-speed rotor technology, which has minimal impact on motor size, flat wire significantly optimizes motor volume. Flat wire technology allows for higher slot fill rates, meaning the same power output can be achieved with a smaller size and less material. This can reduce the motor volume by approximately 30%.
Furthermore, flat wire motors benefit from advanced winding methods, resulting in easier-to-trim motor ends. Compared to round wire motors, flat wire motors reduce end size by 15-20%, further minimizing space and achieving compactness and lightweight.
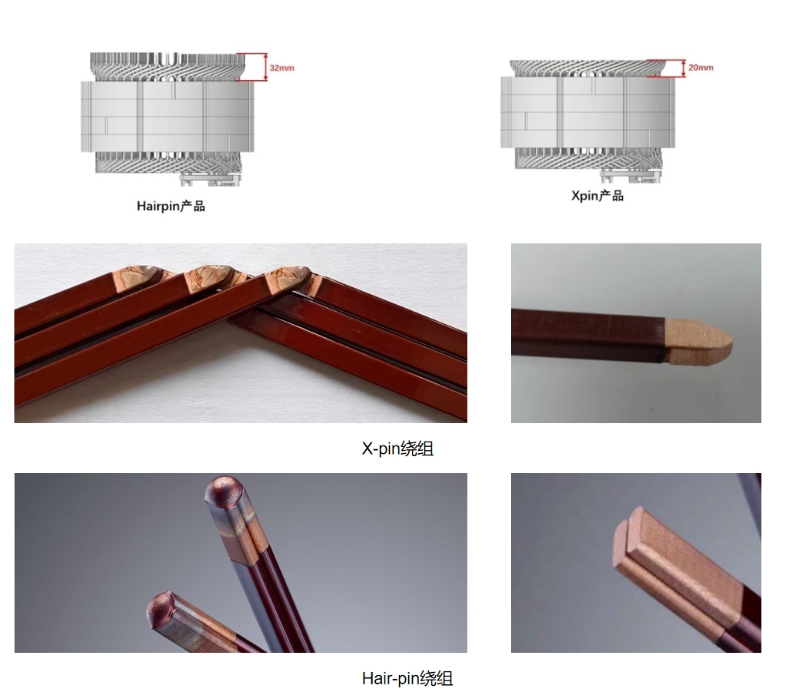
The X-PIN winding takes this a step further by reducing the welding end height from 10mm to just 1mm, compared to Hair-pin’s 7mm. This innovation also addresses the issue of excessive I-pin winding end height, shortening it by 43%. The X-PIN’s closely aligned, slanted arc wires offer higher power density, enabling greater power output in the same volume, making motor winding structures pivotal in optimizing motor size.
6. Material Innovations

Material innovations are key to reducing motor size. Using nanocrystalline and amorphous alloys instead of traditional iron-based electrical steel can significantly enhance motor performance. These materials offer superior magnetic properties, reducing core losses and increasing efficiency. The improved performance of these advanced materials allows for the design of smaller motors with the same or even greater power output. By leveraging material innovations, we can create motors that are both compact and powerful.
Case Study: GAC Aion’s Quark Drive
In 2023, GAC Aion introduced the Quark Drive, a motor that’s only “palm-sized” with a diameter of 180mm and a length of 109mm, yet boasts an impressive power density of 12kW/kg. This is a 100% increase compared to the industry average of 6kW/kg, with an output loss of just 2%, rivaling the power of V8 engines.
Two key innovations stand out in this motor. First, the stator uses a “nanocrystalline-amorphous” alloy material and a mass production process. This technique cools at a rate of up to 1,000,000°C/s, 1000 times faster than traditional iron-based silicon steel. This material’s atomic-level disorder, lack of crystal grains, and absence of grain boundaries significantly reduce core losses compared to conventional materials.
Using this material reduces the motor’s core loss by 50%, enhancing operational efficiency to 97.5%, with peak efficiency reaching 98.5%. Coupled with oil cooling, the motor’s cooling capacity and safety are further improved.
Conclusion
Reducing motor size is a multifaceted challenge that involves increasing power output, utilizing high-speed bearings, improving magnetic flux density, adopting innovative cooling techniques, and leveraging advanced winding technologies and materials. By focusing on these areas, we can create smaller, more efficient motors without sacrificing performance. The advancements seen in motors like GAC Aion’s Quark Drive illustrate the potential of these strategies.
Are you looking to optimize your motor designs? Contact us today to discuss how our custom motor stator laminations can help you achieve smaller, more powerful motors. Let’s work together to innovate and enhance your motor technology!



